Java If else Statement with Examples
In this article, we will be taking a deep dive into the If else statements in the Java programming language. As we proceed through the article, we will be covering the different types of if-else statements and the different types of conditional operators.
We will be covering the different types of if else statements with the help of a flowchart, syntax, and a proper example of a code with output. I suggest you practice the codes shown in the article and also try some variations of the same codes to master the concept.
What are If-Else statements in Java?
If else statements are a type of control flow statements in a programming language. The logic behind them is very simple: If the specified condition is true, then execute a particular set of instructions, and if the given condition is false, then execute another set of instructions.
The if-else statements enable design-making in programming, it helps us write decision-driven statements and executes a particular block of code based on the outcome of a particular condition.
Types of conditional operators in Java
Before we look at the types of if-else statements, let us take a look at the various conditional operators that help us build conditions in programming.
1. Less than: x < y (x is less than y)
2. Greater than: x > y (x is greater than y)
3. Less than or equal to: x <= y (x is less than or equal to y)
4. Greater than or equal to: x >= y (x is Greater than or equal to y)
5. Equal to: x == y (x is equal to y)
6. Not equal to: x != y (x is not equal to y)
Note: in programming languages, a single equal to (=) means assigning, and a double equal to (==) means you are comparing the values of both operands.
Types of If Else Statements in Java
There are four types of If Else statements:
1. If
2. If-Else
3. If-ElseIf-Else
4. Nested If
Let us take a look at each type with the help of a flowchart, syntax, and an example with output.
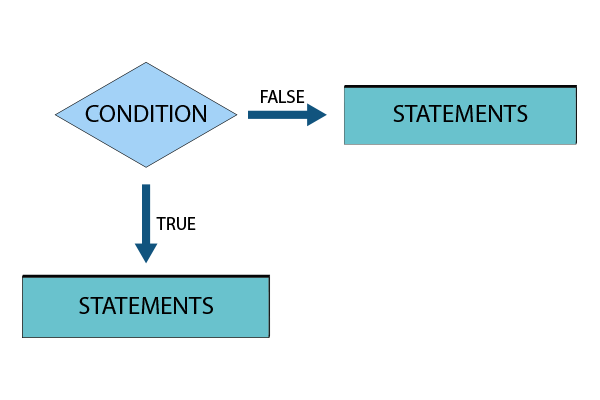
1. Simple If statement
In this type of If-Else statement, If the given condition is true, a set of statements will be executed, and if it is false, nothing gets executed.
Syntax:
If (condition)
{
<statments>
}
Flowchart:
Example:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String x = "FirstCode";
if(x == "FirstCode")
{
System.out.print("The string is FirstCode");
}
}
}
Output:
The string is FirstCode
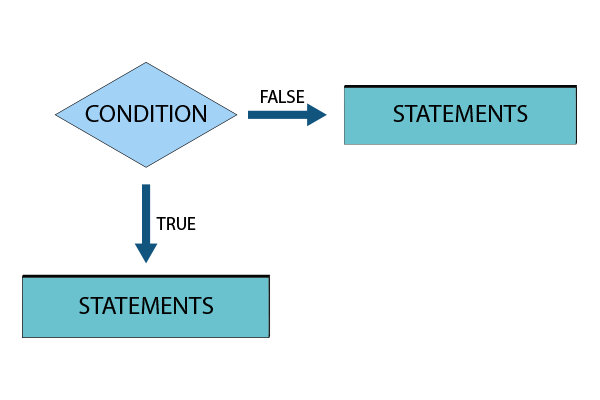
2. If-Else statement
In this type of If-Else statement, If the given condition is true, a set of statements will be executed, and if it is false, another set of instructions will be executed.
Syntax:
If (condition)
{
<statments>
}
Else
{
<statments>
}
Flowchart:
Example:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String x = "Java";
if(x == "FirstCode")
{
System.out.print("The string is FirstCode");
}
else
{
System.out.print("The string is not FirstCode");
}
}
}
Output:
The string is not FirstCode
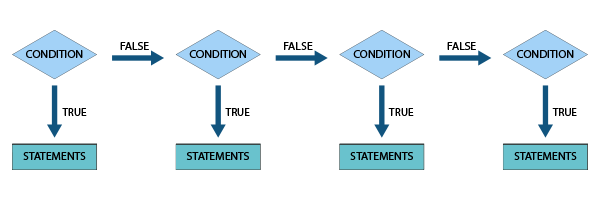
3. If-ElseIf-Else statement
In this type of If-Else statement, If the given condition is true, a set of statements will be executed, and if it is false, another set of instructions will be executed. This process continues in a loop.
Syntax:
If (condition)
{
<statments>
}
ElseIf
{
<statments>
}
Else
{
<statments>
}
Flowchart:
Example:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String x = "Ferarri";
if(x == "FirstCode")
{
System.out.print("The string is FirstCode");
}
else if (x == "Java")
{
System.out.print("The string is Java");
}
else
{
System.out.print("The string is neither FirstCode nor Java");
}
}
}
Output:
The string is neither FirstCode nor Java
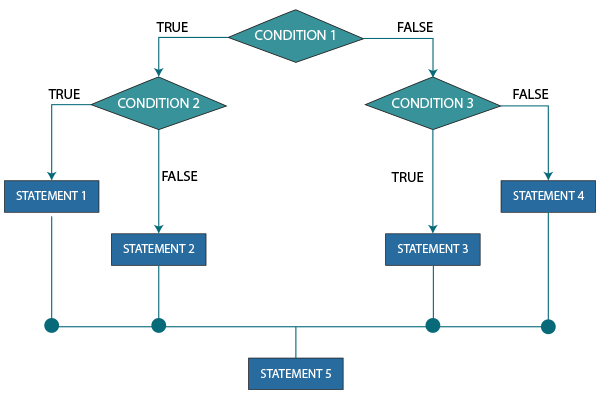
4. Nested If-Else statement
In this type of If-Else statement, we will have an if statement within an if statement.
Syntax:
If (condition)
{
<statments>
If (condition)
{
<statments>
}
Else
{
<statments>
}
}
ElseIf
{
<statments>
}
Else
{
<statments>
}
Flowchart:
Example:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String x = "FirstCode";
int y = 10
if(x == "FirstCode")
{
System.out.print("The string is FirstCode");
if (y > 5)
{
System.out.print("The number is greater than 5");
}
else
{
System.out.print("The number is less than 5");
}
}
else if (x == "Java")
{
System.out.print("The string is Java");
}
else
{
System.out.print("The string is neither FirstCode nor Java");
}
}
}
Output:
The string is FirstCode
The number is greater than 5
Bonus: the ternary operator
Since you stuck around till the end of the article, here is a treat for you: Did you know that you can also write the If-else statement in just one line using a ternary operator? Let us first look at the syntax of the ternary operator:
variable = Expression1 ? Expression2: Expression3
Now let us try to represent the above line using regular If-Else statements:
if(Expression1)
{
variable = Expression2;
}
else
{
variable = Expression3;
}
The ternary operator simply says that if the condition stated in expression one is true, assign the value of expression 2 to the variable, and if the condition in expression 1 is false, assign the variable with the value in expression 3.
Let us look at an example to understand the ternary operator fully:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String x = "First";
String y = "Code";
String z = (x != y) ? (x+y) : (null);
System.out.println("The resultant string is: " + z);
}
}
Output:
The resultant string is FirstCode
Before we finish off, let us write the above code using regular If-Else statements:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String x = "First";
String y = "Code";
String z;
if (x != y)
{
z = (x+y);
}
else
{
z = null;
}
System.out.println("the resultant string is: " + z);
}
}
Output:
The resultant string is FirstCode
Conclusion
You have learned the use of If-Else statements, the various types of conditional operators, and the four types of If-else statements, along with flowcharts, syntax, and an example with output. At the end of the article, we also discussed the ternary operator.